What is the BIEAP Biology Practical Syllabus
Today we are going to talk about the BIEAP Biology Practical Syllabus, for Andhra board 1st year and 2nd year students. We have structured the AP board biology practical syllabus so that it becomes the most comprehensible and can be easily understood and remembered. With the class XI-XII exams 2022 coming soon, both students and teachers can benefit from this comprehensive list of biology practicals. And if you are interested in creating a biology lab for your school in Andhra Pradesh, you can greatly benefit from this list of experiments and observations because it would help you purchase the right biology lab package .

The biology practical exam of BIEAP is conducted by the Andhra Pradesh Board of Intermediate Education near the middle of the year. The list of AP board biology practicals is extensive and has many experiments and observations; and many schools choose not to go through the full syllabus. But that’s not good if you are looking for a future in biosciences. This is because most of the hands-on skills get generated from practical classes only.
Hence, it is best to complete the full BIEAP biology practical syllabus if you’re an Andhra board inter class student of 1st or 2nd year. You can ask your teacher to help you fulfil your syllabus. That being said, many schools are simply not equipped enough to perform all of the experiments and observations in this syllabus. In that case, you can take help from Labkafe Practical Tutorials.
BIEAP Biology Practical Syllabus: Experiment & Observation List
The Andhra board biology practical exam has 30 marks and those marks are distributed in the following way:
- 1 major experiment ‒ 5 marks
- 1 minor experiment ‒ 4 marks
- 1 slide preparation ‒ 5 marks
- Spotting work ‒ 7 marks
- Records and Viva ‒ 4 marks
- Project work ‒ 5 marks
List of Major Experiments
- Carefully study, dissect, and diagram all parts of three commonly available flowers from the following families:
- Solanaceae, Fabaceae and Liliaceae ‒ OR,
- Poaceae, Asteraceae or Brassicaceae (in case the above are not available in that geographic location)
Display the floral whorls, anther, overy, and number of chambers. Also study the plant itself to understand its root type (tap and adventitious), stem type (herbaceous and woody), and leaf (arrangement, shape, venation, simple, compound).
- Study how osmosis occurs using a potato osmometer.
- Macro nutrient tests ‒ detect the presence of sugar, starch, protein and fat in suitable plant and animal samples.
- Paper chromatography test ‒ separate plant pigments using a specialized chromatography paper.

List of Minor Experiments
- Transpiration experiment ‒ study and compare how a leaf of a plant performs transpiration through the upper and the lower side of the leaf.
- Study the rate of respiration in one of the following:
- Flower buds
- Leaf tissues
- Germinating seeds
- Urine tests ‒ determine the presence of the following in urine:
- Urea
- Sugar
- Albumin
- Bile salts
List of Slide Preparation
- Studying the transverse sections of monocot and dicot roots and primary stems.
- Preparing an epidermal peel of rhoeo leaves and observing plasmolysis in it.
- Preparing a T.S. of a leaf and thereby observing the presence of stomata in the upper and lower surface of the leaf.
Spotting Work
- Learn the parts of a microscope and how to work them.
- Learn to identify the following models, specimens and prepared slides:
- Bacteria, Oscillatoria, Spirogyra, Rhizopus, mushroom, yeast, liverwort, moss, fern, pine, monocotyledonous plant, dicotyledonous plant and lichen.
- Learn to identify the following specimens, prepared slides, or virtual models:
- Amoeba, Hydra, liver fluke, Ascaris, leech, earthworm, prawn, silkworm, honeybee, snail, starfish, shark, rohu, frog, lizard, pigeon and rabbit.
- Use prepared or temporary slides to study the shapes and sizes of the following types of tissues:
- palisade cells, guard cells, parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, xylem, phloem, squamous epithelium, muscle fibres and mammalian blood smear
- Study how mitosis occurs in plant and animal cells, using onion root tip cells and grasshopper cells.
- Learn to identify the various types of modification that happen in nature to plant bodies ‒ root, stem and leaf modification study.
- Study inflorescence (how flowers are arranged) on branches with cymose and racemose types.
- Study how imbibition occurs in seeds and raisins.
- Learn the setting up of the following three experiments:
- Anaerobic respiration
- Phototropism
- Effect of apical bud removal
- Use a model skeleton, charts, and illustrations to understand the different bones and joints of the human skeleton.
- Use virtual models or images to study the external morphology of a cockroach.

How to do Andhra Board Biology Practicals
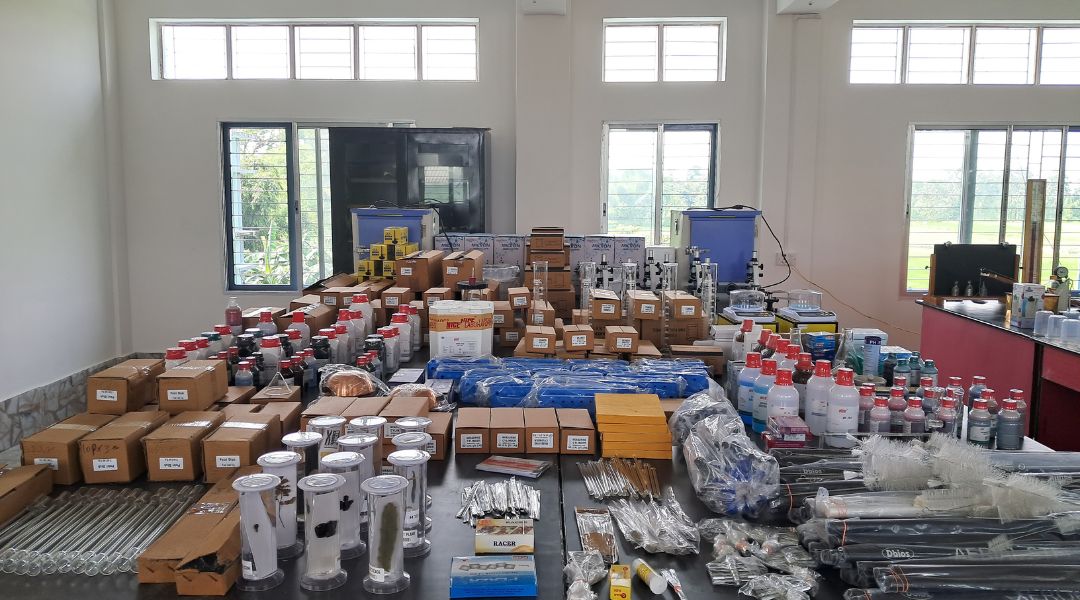
The BIEAP biology practical syllabus has quite a lot of stuff in it; however, don’t fret. All of the above experiments, preparations, and observations are possible with Labkafe’s BIEAP Biology Lab Equipment Package. This customized laboratory equipment package has everything you need to perform those works ‒ glassware, reagents, support apparatus, models, specimens, charts ‒ all you’d ever need to cover the syllabus.
Labkafe aims to bring affordable practical education to every child in India as well as Andhra Pradesh; as such, we prepare custom lab equipment packages for all types of laboratories working under all boards and disciplines. For primary, secondary, and higher secondary schools, this includes lab packages for physics, chemistry, biology, maths, robotics, astronomy, drone labs, IoT, and more. We have a national reach in over 1200 schools, colleges, and research institutes ‒ and we boast a strong presence on GeM procurement as well.







Leave a Reply