Table of Contents
- Types of Biosafety Cabinets
- What are Biosafety Cabinets Used For?
- 1. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Microbiology
- 2. Medical Research Warrants the Use of Biosafety Cabinets
- 3. Pharmaceutical Laboratories Use Class III Biosafety Cabinets
- 4. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Diagnostic Labs
- 5. Safe Research in Biotechnology Requires Laboratory Hoods
- 6. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Vaccine Development
- 7. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Cell Culture Labs
- 8. Lead Shielded Cabinets for Radiopharmaceutical Applications
- 9. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Environmental Research
- Conclusion
Biosafety cabinet uses in Microbiology, Medical Research, Pharmaceutical Laboratories, Diagnostic Laboratories, Biotechnology, Vaccine Development, Tissue Culture, Radiopharmaceuticals and Environmental Science are diverse.
Let’s explore the various use cases and understand if you need a biosafety cabinet to perform your lab work safely.
Types of Biosafety Cabinets
Biosafety Cabinet (BSC) Class I
- User & Environment Protection: Protects the operator and environment only; does not protect the sample.
- Airflow & Filtration: Inward airflow captures aerosols, then passes through a pre-filter and HEPA filter before exhaust.
- Applications: Limited use due to risk of cross-contamination; unsuitable for sterile work.
- Status: Mostly outdated and replaced by Class II cabinets.
BSC Class II
- User & Environment Protection: Protects the operator, environment, and the sample.
- Airflow & Filtration:
- Inflow air protects the user from hazardous materials.
- HEPA/ULPA-filtered downflow maintains a sterile ISO Class 3 work surface.
- HEPA/ULPA-filtered exhaust protects the environment.
- Inflow air protects the user from hazardous materials.
- Applications: Suitable for microbiology, pharmaceuticals, and biomedical research; commonly used in schools and research labs.
- Types:
- Type A1: 70% recirculated, 30% exhausted; for BSL-1 to BSL-3 agents.
- Type A2: Most common type; similar airflow to A1.
- Type B1: 70% exhausted, 30% recirculated; for small quantities of volatile toxic chemicals.
- Type B2: 100% exhausted (no recirculation); ideal for toxic chemical use.
- Type A1: 70% recirculated, 30% exhausted; for BSL-1 to BSL-3 agents.
BSC Class III
- User & Environment Protection: Provides complete protection for the operator, environment, and sample.
- Airflow & Filtration:
- Operates under negative pressure for maximum containment.
- Exhaust air is HEPA-filtered and incinerated for enhanced safety.
- Operates under negative pressure for maximum containment.
- Applications: Suitable for high-risk work, including Risk Group 4 pathogens.
- Design Features:
- Fully enclosed, gas-tight metal construction.
- Glove ports for safe handling.
- Pass-through units for secure material transfer.
- Air exhaust directed through a duct system or filtered back into the lab.
- Fully enclosed, gas-tight metal construction.
What are Biosafety Cabinets Used For?

Biosafety cabinets find uses in many fields:
1. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Microbiology
- Biosafety cabinets help handle pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and fungi in microbiology labs.
- Streak plating, active culture and broth culture, handling hazardous microorganisms, and colony counting are common uses for Class II and III cabinets.
- Class II and III cabinets protect users from bacterial samples and also shield the sample from contamination by the environment. They also protect other people in the lab, as the air exiting the cabinet passes through a HEPA filter before release.
- Class I biosafety cabinets are typically used to enclose specific equipment like centrifuges or for tasks like aerating cultures that may generate aerosols. These cabinets offer protection to the operator, and the outgoing air is sterilized via HEPA filters before it is discharged. The exhaust HEPA filter removes only airborne aerosols and biohazards—not chemical fumes.
- For the most dangerous pathogens, Class III cabinets are required, as they can handle biosafety level 1, 2, 3, and 4 pathogens effectively.
2. Medical Research Warrants the Use of Biosafety Cabinets
- Medical Researchers analyze patient samples to study disease pathology and strain type. This helps link symptoms to the pathogen and develop treatments or vaccines.
- For example: Ebola was first identified in 1976, with early classification aided by the London School of Tropical Medicine.
- High-risk pathogens like Ebola require BSL-3 or BSL-4 containment. Class III biosafety cabinets are used for such samples to protect researchers and the lab environment.
3. Pharmaceutical Laboratories Use Class III Biosafety Cabinets
- Experiments involving active molecules aim to neutralize harmful pathogens or bacteria, especially those with evolving antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria and viruses that do not respond to conventional treatment need special test protocols within BSCs.
- Testing these molecules requires exposing them to the pathogens, which are dangerous to humans. Therefore, such work must be conducted inside a Class III biosafety cabinet to ensure maximum containment and user safety.
- Pharmaceutical preparation also requires sterile, controlled environments like clean rooms and biosafety cabinets. Tasks include preparing sterile injectable medications (e.g., chemotherapy drugs, IV antibiotics), compounding total parenteral nutrition (TPN) solutions, and monoclonal antibodies.
4. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Diagnostic Labs

- Diagnostic Labs handle body fluids like blood, saliva, stool, and semen that may carry infections.
- These samples may contain zoonotic viruses or dangerous pathogens like HIV, tuberculosis, or emerging viruses such as SARS-CoV-2.
- Many of these viruses originate in lesser-known zoonotic reservoirs and pose serious threats to humans.
- Investigation and research on such pathogens is necessary but risky, requiring strict containment.
- Therefore, Class III biosafety cabinets are essential to protect technicians during sample handling and testing.
5. Safe Research in Biotechnology Requires Laboratory Hoods

- Biotechnology research laboratories must prevent the dispersal of genetic material from hazardous organisms into the environment. Carry out genetic engineering work involving recombinant DNA or CRISPR technologies safely inside biosafety cabinets.
- Infectious proteins and RNA-based agents like prions and certain viral genomes must be handled only in Class III biosafety cabinets.
- Enclose specific equipment like centrifuges or conduct procedures like aerating cultures in Class I biosafety cabinets to prevent spread of infectious aerosols in the lab environment.
6. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Vaccine Development
- Work involving high-risk Group 4 pathogenic organisms requires maximum containment, typically in Class III biosafety cabinets.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, Class II Type A2 BSCs proved effective for safely handling samples, offering strong protection for both users and the environment.
- These cabinets helped maintain biosafety standards and safeguard public health during widespread testing and research.
7. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Cell Culture Labs

- Selecting and isolating cell lines like pluripotent stem cells and animal cell lines requires a sterile environment, as nascent cell lines are highly prone to contamination. In plant meristem culture, BSCs prevent fungal and bacterial contamination during excision of apical meristems, ensuring virus-free plant propagation.
- In CAR T-cell therapy, BSCs help prevent cross-contamination between samples during genetic modification and expansion phases.
- A Class II biosafety cabinet is needed during processes like trypsinization and splitting of cell lines.
- Extremely sensitive cell lines such as Primary Bovine Thyroid (BTY) and Vero cell lines require Class III cabinets for better protection.
8. Lead Shielded Cabinets for Radiopharmaceutical Applications
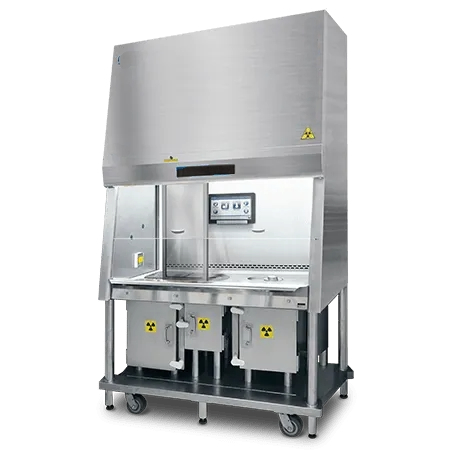

- Shielded Biological Safety Cabinets (BSCs) are designed for radiopharmaceutical preparation, providing radiation protection through lead lining and stainless steel interiors for easy decontamination.
- Class II Type B2 BSCs are used for handling biological radioactive materials that contain a radioactive substance in association with one or more other ingredients that are intended to diagnose, stage a disease, monitor treatment, or provide therapy.
9. Biosafety Cabinet Uses in Environmental Research

- Sampling bacteria from natural habitats and mangroves helps identify microorganisms that may cause diseases or pose environmental risks to humans and animals. These require biosafety cabinets to protect the researchers in case the bacteria is pathogenic.
- Researchers study these microbes to understand their ecological interactions and roles within ecosystems, especially in relation to public and environmental health.
- Food and water samples are also analyzed in such labs, to trace sources of microbial contamination.
Conclusion
Biosafety cabinets are essential in labs handling infectious agents, ensuring user, sample, and environmental safety. They are widely used in microbiology, medical research, pharmaceutical testing, diagnostics, biotechnology, vaccine development, tissue culture, radiopharmaceuticals, and environmental science. Class I cabinets handle aerosol-generating tasks, while Class II and III provide advanced protection for high-risk pathogens and sterile processes. From studying deadly viruses like Ebola to developing vaccines or working with genetically modified organisms, BSCs maintain strict containment and sterile conditions across various scientific fields.
Looking for reliable biosafety cabinets for your lab? Explore our range of Class I, II, and III cabinets designed for safety and performance. Contact us today to place your order or learn more!












Leave a Reply