Table of Contents
- What is Solar Energy?
- How is Solar Energy Stored or Harvested?
- Transformation of Solar Energy
- Understanding Transformation of Energy Using Solar Energy Demonstration Models
- Benefits of Solar Energy Demonstration Models by Labkafe
The Sun produces solar energy. In such large amounts, that we could solve the world’s energy demand with it. Man harvests, stores and transforms solar energy for so many uses. Our solar demonstration models will teach you how.
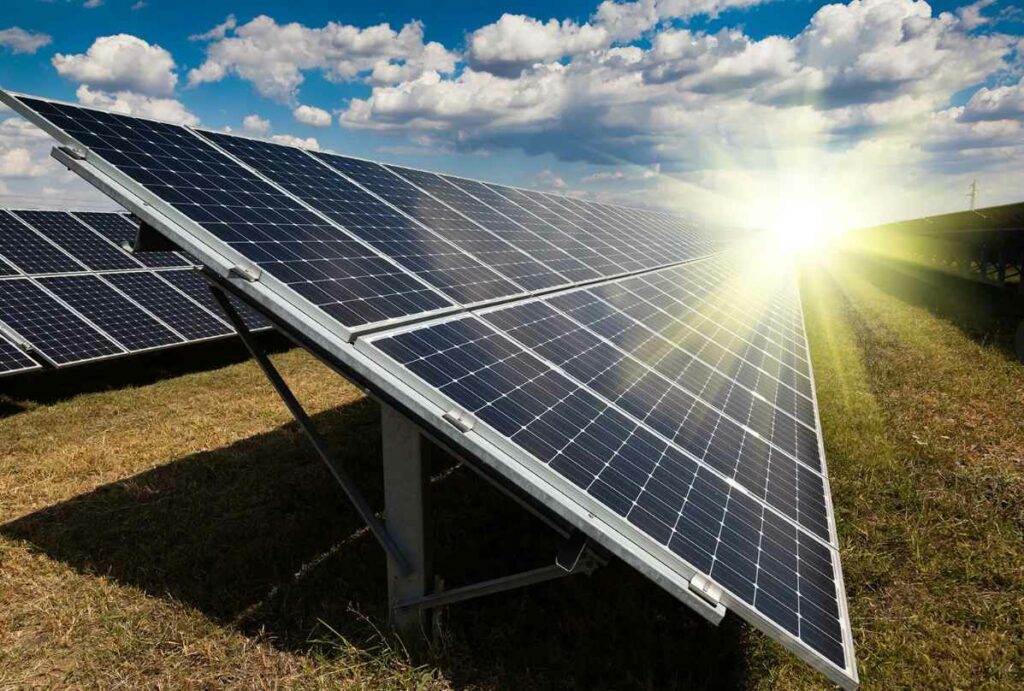

What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the energy that the sun radiates. It travels towards the sun in the form of light rays. This can be converted into various other forms of energy for consumption and use. The amount of energy radiated by the Sun is vastly in excess of global energy demand. Hence, it is a good source of renewable energy that can be converted into other forms of energy for use in various applications.
How is Solar Energy Stored or Harvested?
Solar energy is radiated and incident on the Earth’s surface as light energy. It cannot directly be used for any applications, other than illumination during daytime or reading under the sun. To properly utilize solar energy, it must be harvested, stored and transformed into other forms of energy.
How to Harvest It?
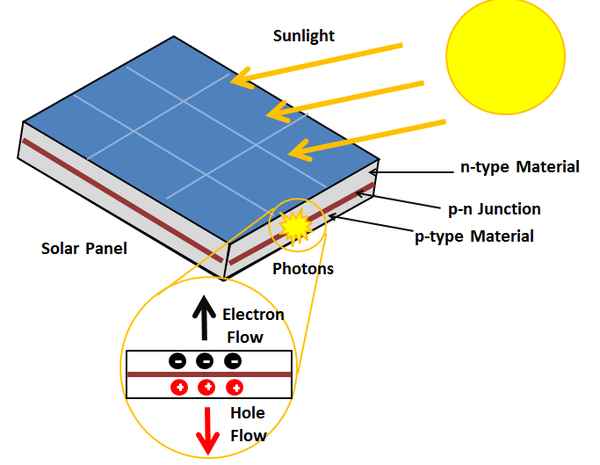
Photovoltaic (PV) Panels are the most common method of harvesting solar energy today:
- These panels consist of many PV cells arranged in a matrix, ranging from a few cm² to several m² in size.
- Larger surface areas allow more sunlight to hit the PV cells, resulting in higher energy output.
- Each PV cell contains two semiconductor wafers—one P-type and one N-type—usually made of monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon.
- When stacked, these wafers form a depletion zone that initially remains in electrical equilibrium.
- As sunlight photons strike the PV cell, they disrupt the depletion zone, creating a flow of electricity.
- This photon interaction happens continuously in sunlight, generating direct current (DC) electricity.
- Multiple PV cells combine to form a solar panel, and many panels create a solar array, significantly increasing power output.
- Since modern appliances use alternating current (AC), the DC output from solar panels must be converted using an inverter.
- Various advanced technologies aim to improve PV cell efficiency, panel construction, and system integration.
Why Do You Need to Store It?
Storing solar energy is essential because it ensures continuous power availability, especially during nighttime or cloudy conditions. It allows users to save surplus energy when demand is low and use it later when demand is high, which helps stabilize the grid and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, solar energy storage increases energy independence, protects against outages, lowers electricity bills in areas with time-based utility rates, and supports efficient use of solar power even when net metering policies are limited.
How Can You Store It?
- Battery Storage: The most common residential method, it stores solar energy through chemical reactions inside lithium-ion batteries. When needed, the stored energy is released as electricity, offering quick and reliable power.
- Thermal Storage: This method stores solar heat in materials like water or molten salt. The retained heat can later be used to produce steam for power generation, especially useful in solar thermal plants.
- Mechanical Storage: It converts solar power into mechanical energy using systems like flywheels, pumped hydro, or compressed air, then reverts it to electricity during high demand periods.
Transformation of Solar Energy
Solar energy needs to be transformed into other forms for consumption and use in various daily uses and applications. Let’s look into various methods by which solar energy is transformed into other forms of energy and used in daily applications.
Photovoltaic Systems
Photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect in semiconductor materials, typically silicon. When photons strike the cell, they dislodge electrons from atoms, creating an electric current. This direct conversion process makes PV systems one of the most versatile and widely deployed solar technologies globally.
Solar Thermal Systems
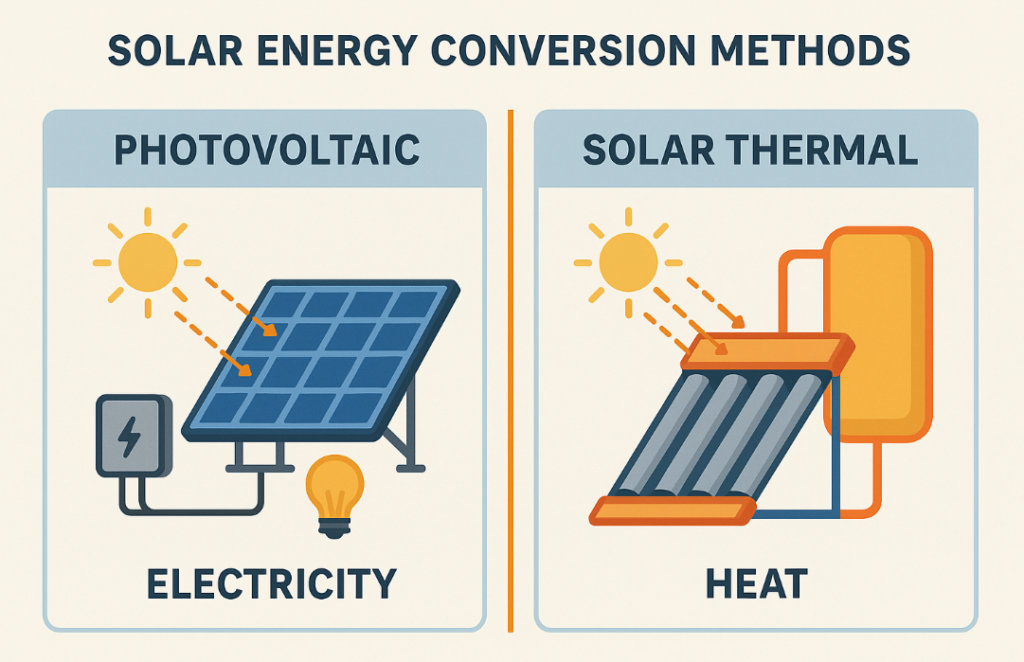
Solar thermal systems convert sunlight into thermal energy (heat) by absorbing solar radiation to heat a fluid, which can then be used for various heating applications or to generate electricity. Unlike photovoltaics, these systems capture the heat energy from sunlight rather than converting it directly to electricity.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
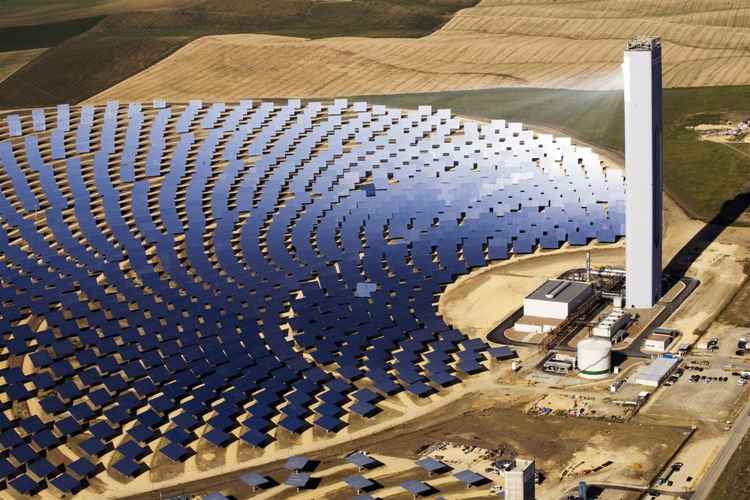

CSP uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a small receiver, generating high temperatures that can produce steam to drive turbines for electricity generation. This approach allows for both electricity production and thermal energy storage, making it a versatile technology for utility-scale applications.
Understanding Transformation of Energy Using Solar Energy Demonstration Models
A solar energy setup in India costs a minimum of INR 1.5 lakhs (Bluebird Solar). Hence, visualizing and understanding solar energy harvesting, storage, and transformation often remains a theoretical experience for students in India.
This is where the Labkafe solar demonstration models come in. Built in high-quality, durable wooden settings, these models effectively demonstrate the harvesting, storage, and transformation of solar energy. They allow teachers to help students practically understand solar energy dynamics on a small to medium scale. Without the need for a field visit, this is the closest one can get to a hands-on solar energy demonstration.
1. Solar Fan Demonstration Model
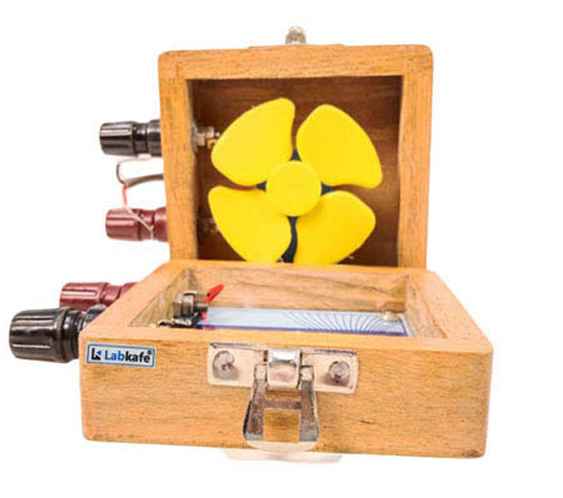

This model is enclosed in a two-part wooden case. One part has a solar cell, and the other has a fan.
- How it works: When sunlight strikes the solar cell, it converts solar energy into electrical energy using the photovoltaic effect. This current flows through wires to a small DC motor attached to the fan. The motor converts electrical energy into kinetic energy, causing the fan blades to rotate.
- Energy conversion:
Solar energy → Electrical energy (via solar cell) → Kinetic energy (via DC motor)
2. Solar Energy Demonstration Models: Light, Sound, Movement & Voltage

This all-in-one wooden box contains a solar panel, rechargeable cell, LED, music buzzer, fan, and voltmeter.
- How it works:
- The solar panel captures sunlight and converts it into electrical energy.
- This energy either powers the devices directly or charges the rechargeable battery for later use.
- The LED transforms electrical energy into light energy.
- The music buzzer converts it into sound energy.
- The fan uses a small motor to turn electrical energy into kinetic energy.
- The voltmeter measures the voltage produced by the solar panel in real-time.
- The solar panel captures sunlight and converts it into electrical energy.
- Energy conversions:
Solar energy → Electrical energy →
• Light energy (via LED)
• Sound energy (via buzzer)
• Kinetic energy (via fan motor)
• Stored energy (via rechargeable cell)
3. Solar Water Heater Demonstration Model
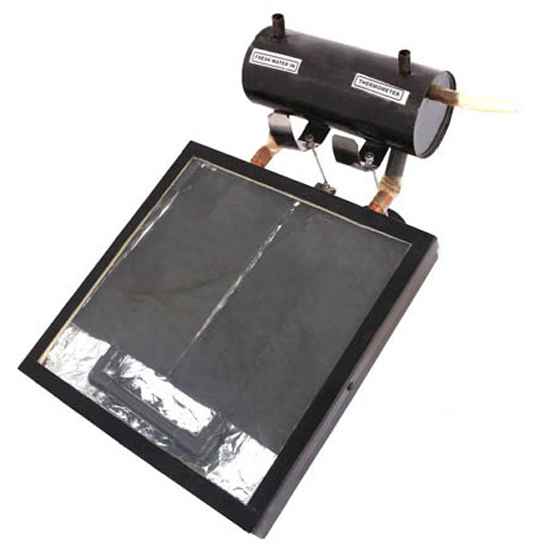

This device demonstrates the heating of water using sunlight. It includes black copper pipes, a glass cover, a water tank, thermometer and funnel.
- How it works:
- Sunlight enters through the glass sheet, which creates a greenhouse effect.
- The black-painted copper pipes absorb solar radiation and become hot due to their high thermal conductivity and black surface.
- Water flows through these pipes, absorbing the heat and increasing in temperature.
- The heated water rises and is collected in the storage tank.
- Sunlight enters through the glass sheet, which creates a greenhouse effect.
- Energy conversion:
Solar energy → Thermal energy (absorbed by copper pipes) → Thermal energy transferred to water
4. Solar Water Pump Demonstration Model

This model consists of a solar panel, DC motor, and a mini water pump with tubing.
- How it works:
- The solar panel converts sunlight into electrical energy.
- This electricity powers a DC motor, which rotates a pump impeller.
- As the impeller spins, it creates pressure that lifts and pushes water through the attached tube, resulting in a spray or flow of water.
- The solar panel converts sunlight into electrical energy.
- Energy conversion:
Solar energy → Electrical energy → Kinetic energy (impeller) → Mechanical energy (water flow)
5. Solar Cooker Demonstration Model
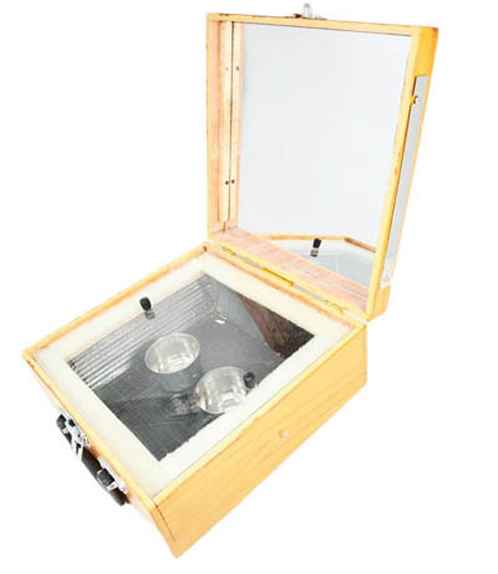

This cooker includes a wooden and metal body with a glass cover and an insulated interior.
- How it works:
- Sunlight enters through the glass cover and is absorbed by the interior metallic surface and cooking vessel.
- These surfaces convert solar energy into thermal energy.
- The transparent glass cover traps the heat inside (greenhouse effect), slowly cooking the food.
- Because the cooking is slow and uses indirect heat, nutrients and vitamins in the food remain largely intact.
- Sunlight enters through the glass cover and is absorbed by the interior metallic surface and cooking vessel.
- Energy conversion:
Solar energy → Thermal energy (retained in the cooking chamber)
Benefits of Solar Energy Demonstration Models by Labkafe
At Labkafe, we’re dedicated to transforming how science is taught across India. With years of hands-on experience and a strong presence in the education sector, we deliver reliable, affordable, and innovative lab solutions to institutions of all sizes. Here’s what makes us stand out:
- Extensive Product Range – 12,000+ lab equipment and apparatus designed for school to college-level use.
- Trusted Nationwide – Successfully transformed 1,800+ institutions, including IITs, NITs, and top private schools like Don Bosco & St. James’.
- Impact at All Levels – Serving learners from grade 6 to advanced research scholars through domain-specific tools.
With this unmatched experience and reach, you can rely on Labkafe’s solar energy demonstration models to be accurate, durable, and highly effective for classroom demonstration and learning.












Leave a Reply