Table of Contents
- Why Optimum Air Quality in Workspaces is Not Optional
- 1. Contaminant Control Method: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
- 2. Efficiency in Removing Hazards: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
- 3. Scope of Application: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
- 4. Design and Installation Requirements
- 5. Energy Consumption: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
- 6. Effect on Air Distribution: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
- 7. Suitability for Hazardous Processes
- 8. Impact on Indoor Air Quality
- 9. Maintenance and Durability
- 10. Training and Monitoring
- Which One Should You Choose: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Optimum Air Quality in Workspaces is Not Optional

Local exhaust ventilation vs general ventilation: Poor indoor air quality is a serious problem in many workplaces. From welding fumes to dust, smoke, vapors, and other airborne contaminants, workers are constantly exposed to hazards that may not be visible but can cause long-term health damage. Traditional ventilation methods like opening windows or using ceiling fans may not be enough. That’s where local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems come in. Unlike general ventilation, which works by diluting air contaminants throughout the room, LEV systems target harmful substances right at the source and remove them before they spread. But how exactly do they differ?
Here’s a 10-point comparison that will help you decide which solution is ideal for your environment.
1. Contaminant Control Method: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
General ventilation dilutes airborne contaminants throughout the entire space. This works best in low-contamination environments like schools or offices.
Local exhaust ventilation, however, captures contaminants directly at the source before they mix with indoor air. It prevents the spread of toxic substances and is essential in places where dangerous gases, dust, or fumes are released.
2. Efficiency in Removing Hazards: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
Local exhaust ventilation is significantly more efficient when it comes to removing specific hazards. It is engineered for targeted extraction and ensures quick removal of harmful substances.
General ventilation may reduce the overall concentration but cannot guarantee safety in high-risk areas where toxic emissions are present.
3. Scope of Application: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
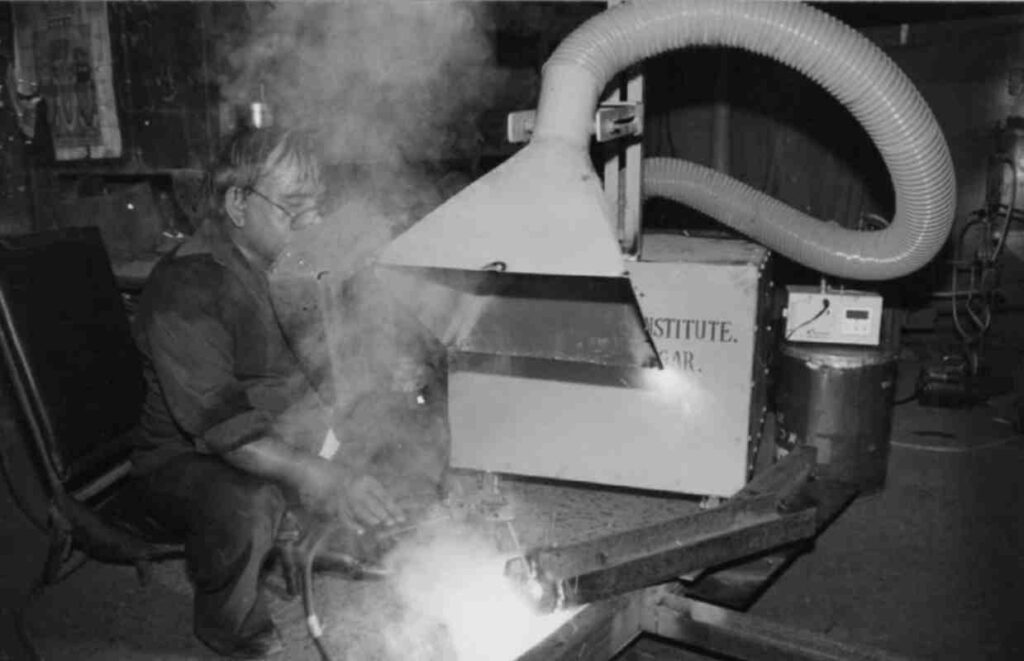

Use general ventilation in larger, less hazardous environments where low levels of pollutants are released intermittently.
On the other hand, local exhaust ventilation is crucial in industries such as welding, milling, woodworking, electric arc, electronics, laser cutting, and 3D printing—where even minor particles can cause serious issues in production or health.
4. Design and Installation Requirements
General ventilation systems are easier and cheaper to install. They involve natural airflow or mechanical systems that circulate air through the room.
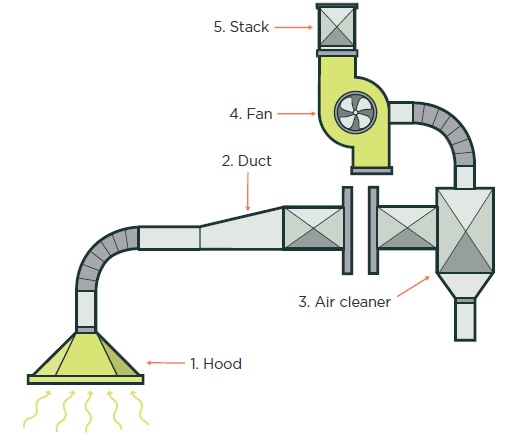
Local exhaust ventilation systems require a carefully engineered setup including:
- Capture hoods to trap contaminants at the source
- Ductwork to carry contaminated air
- Air cleaning devices (if needed)
- Exhaust fans
- Exhaust stacks for safe discharge
Because of the complexity, only trained professionals should handle their design and modification.
5. Energy Consumption: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation
General ventilation often uses more energy to move and dilute large volumes of air.
Local exhaust ventilation, by focusing only on the contaminated area, is generally more energy-efficient, making it a cost-effective option in the long term.
6. Effect on Air Distribution: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation

General ventilation may unintentionally spread contaminants throughout the room before they are vented out, which can increase exposure risks.
In contrast, local exhaust ventilation prevents this by capturing and removing pollutants before they can disperse.
7. Suitability for Hazardous Processes
General ventilation is unsuitable for hazardous processes involving toxic fumes or flammable gases.
Local exhaust ventilation is necessary in operations like:
- Labs that work with pathogens or toxic fumes
- Welding (removal of metal fumes)
- Paint spraying (removal of vapors)
- Chemical processing (removal of harmful gases)
- Stone or marble cutting (removal of fine dust)
8. Impact on Indoor Air Quality
General ventilation improves overall air quality but may fail to protect workers near the source of contamination.
Local exhaust ventilation dramatically reduces exposure near hazardous processes, contributing to a safer and more breathable environment for those working close to pollutants.
9. Maintenance and Durability
General ventilation systems need less upkeep and are more forgiving over time.
Local exhaust ventilation systems require regular maintenance and routine testing because contaminants, especially in filters, can build up. Their performance can decline without timely checks and proper care.
10. Training and Monitoring
General ventilation usually does not require special training to operate or monitor.
However, for local exhaust ventilation, employers must ensure:
- Proper installation by qualified personnel
- Periodic performance checks
- Staff training on usage
- No unauthorized modifications
Find a trusted training resource here: HSENI LEV Guide
Which One Should You Choose: Local Exhaust Ventilation vs General Ventilation?
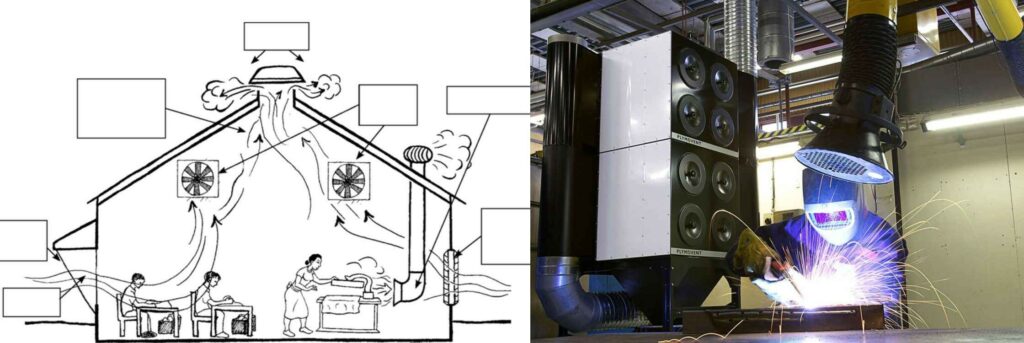
If you’re managing a low-contamination environment like a school or general office, general ventilation may be sufficient to maintain air quality. But if your laboratory involves hazardous materials, fine dust, vapors, or toxic fumes—local exhaust ventilation is not just ideal, it’s essential.
At Labkafe, we specialize in providing advanced local exhaust ventilation systems designed for safety, efficiency, and durability. Whether it’s for chemical labs, biological labs, electronics labs or anatomy labs, we have a solution tailored to your needs.
Improve air quality. Reduce health risks. Protect your workforce. Choose Labkafe.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is local exhaust ventilation?
Local exhaust ventilation (LEV) is an engineered system that captures and removes harmful airborne contaminants—like dust, fumes, or vapors—directly at their source before they spread through the workspace.
Q2: What is the difference between GEV and LEV?
General ventilation (GEV) dilutes contaminants across a large area using natural or mechanical airflow. LEV targets contaminants at the source and removes them directly, making it more effective for hazardous processes.
Q3: What is the difference between an exhaust system and a ventilation system?
A ventilation system controls air movement within a space to maintain air quality. An exhaust system, like LEV, is a type of ventilation specifically designed to remove contaminated air from the source and discharge it outside.












Leave a Reply