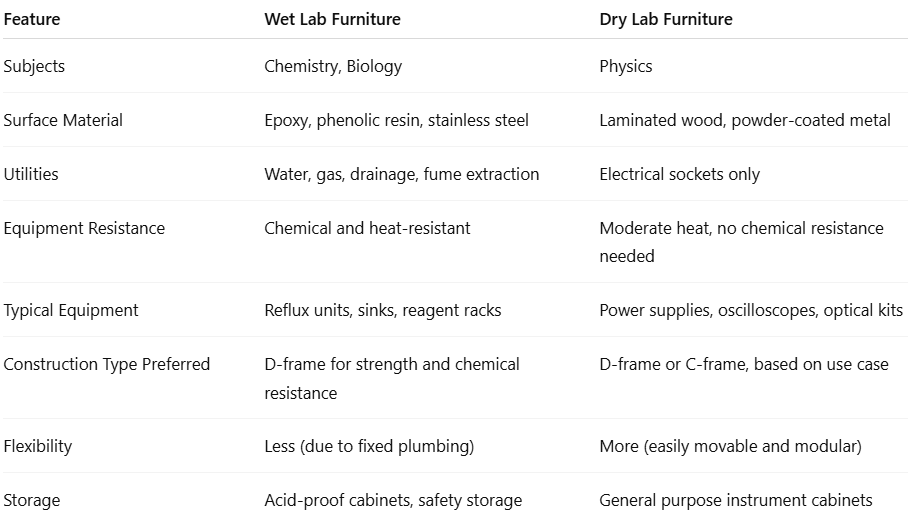
Schools must carefully consider the type of laboratory furniture when designing labs. The requirements for wet and dry lab furniture are significantly different because the nature of experiments, equipment, and safety considerations vary widely across subjects. Let’s explore how wet vs dry lab furniture differs, especially in the school setting.
Understanding Wet vs Dry Labs in Schools
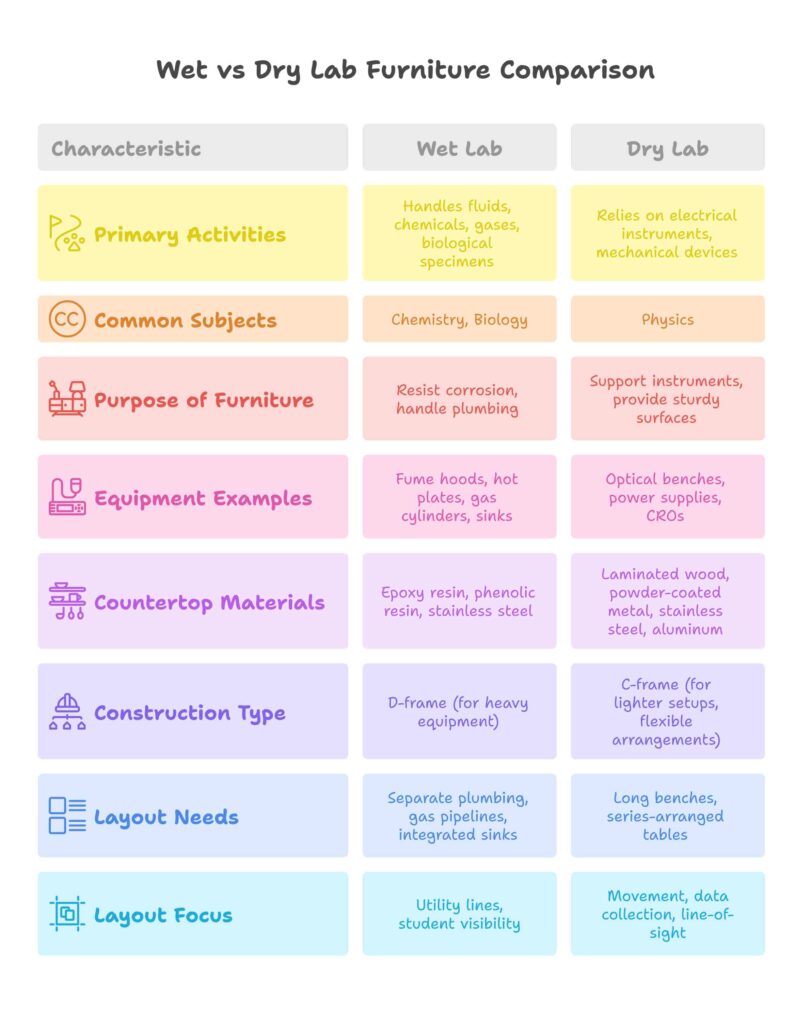
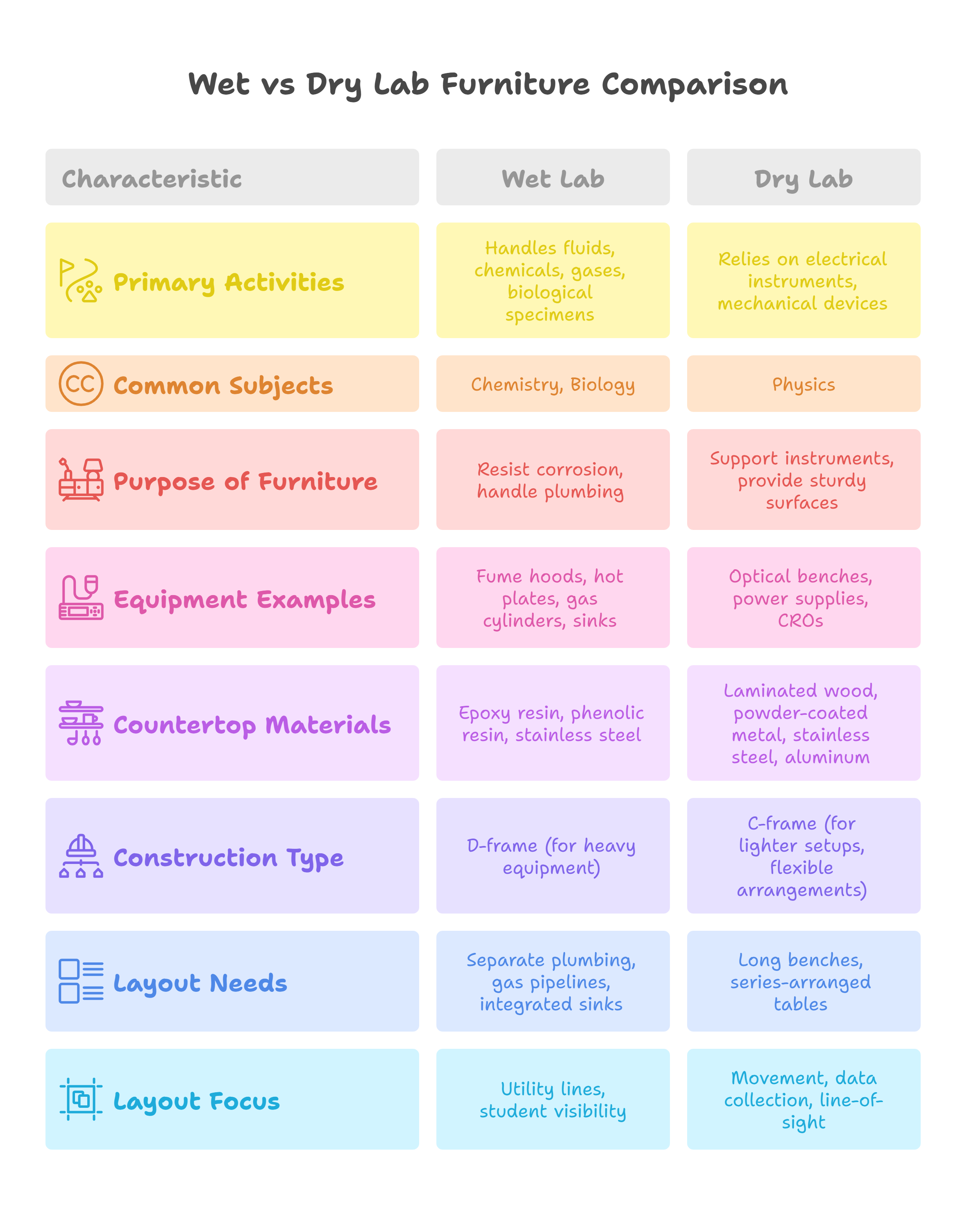
Wet labs handle fluids, chemicals, gases, and biological specimens. These are commonly found in chemistry and biology labs. On the other hand, dry labs, like most physics labs, rarely use liquids. Instead, they rely on electrical instruments and mechanical devices for measurement, data collection, and verification of physical principles.
Purpose of Lab Furniture: Wet vs Dry Lab Furniture
The design of lab furniture directly supports the function of the lab.
- In wet labs, the furniture must resist corrosion from chemicals and handle plumbing for water and gas.
- In dry labs, the furniture should support delicate electrical instruments and provide sturdy surfaces for physical experiments.
Differences Based on School Lab Equipment: Wet vs Dry Lab Furniture
Equipment Used in Physics (Dry) Labs
Physics labs in schools use several types of apparatus that do not require chemical resistance but do demand sturdy work surfaces. Some examples include:
- Optical benches
- DC regulated power supplies
- Transformer coil setups
- CROs (Cathode Ray Oscilloscopes)
- Motor-generator kits
- Air tracks or frictionless motion setups
- Pendulum stands with heavy metal bases
- Vibration magnetometers
- Beam balances with cast-iron bases
These instruments require robust benches that can support weight without chemical resistance. Worktops made of laminated wood or powder-coated metal usually suffice. However, for better fire safety, stainless steel or aluminum tops are preferable.
Equipment Used in Chemistry (Wet) Labs
Chemistry labs deal with acids, bases, and volatile substances. Hence, lab furniture must resist corrosion and accommodate gas and water connections. Examples of common equipment include:
- Fume hoods
- Electric hot plates or heating mantles
- Gas cylinders with regulators
- Reflux and distillation units
- Desiccators
- Water baths with heaters
- Lab sinks with proper drainage
- Storage cupboards resistant to acids and bases
To withstand harsh chemicals like HCl, NaOH, or H₂SO₄, surfaces must be made from epoxy resin, phenolic resin, high-pressure laminate, or stainless steel. While granite is used, its porous surface can be damaged by stagnant water unless coated properly.
Best countertop materials for wet lab benches:
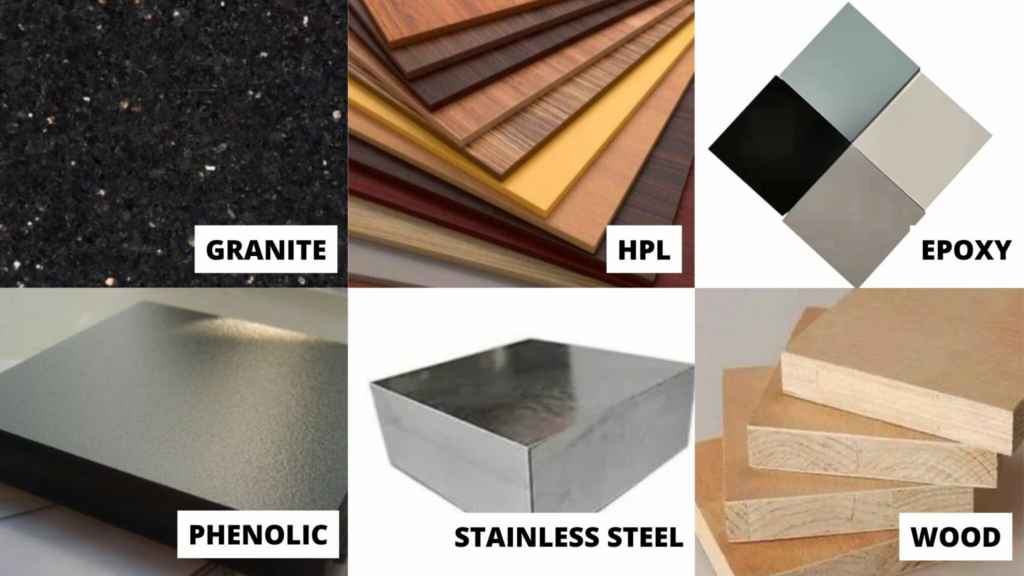

- Epoxy resin
- Phenolic resin
- Stainless steel
These ensure maximum resistance to corrosion, fire, and long-term wear.
Equipment Used in Biology Labs
Biology labs in schools are also considered wet labs. Common equipment includes:
- Compound microscopes
- Projection microscopes (optional)
- Benchtop incubators
- Sterilizers and autoclaves
- Basic centrifuges (rare in schools)
Though not as chemically intensive as chemistry labs, biology labs still need water access and moisture-resistant surfaces. Therefore, their furniture should also be able to resist water and light chemical exposure.
CBSE Composite Science Labs: Wet and Dry Lab Furniture
CBSE-affiliated schools often use composite science labs for Classes 9 and 10. These labs combine physics, chemistry, and biology in one space. Thus, they must be equipped for both wet and dry lab activities. Essential features include:
- Integrated sinks and burners
- Gas lines for heating setups
- Acid/base-resistant benchtops
- Electrical panels for physics experiments
- Storage cupboards for chemicals and equipment
- Table-mounted reagent racks
Furniture in such labs must support diverse equipment while maintaining flexibility in layout. Stainless steel or epoxy-coated surfaces and modular benches work best here.
Wet vs Dry Lab Furniture Construction: D-Frame vs C-Frame
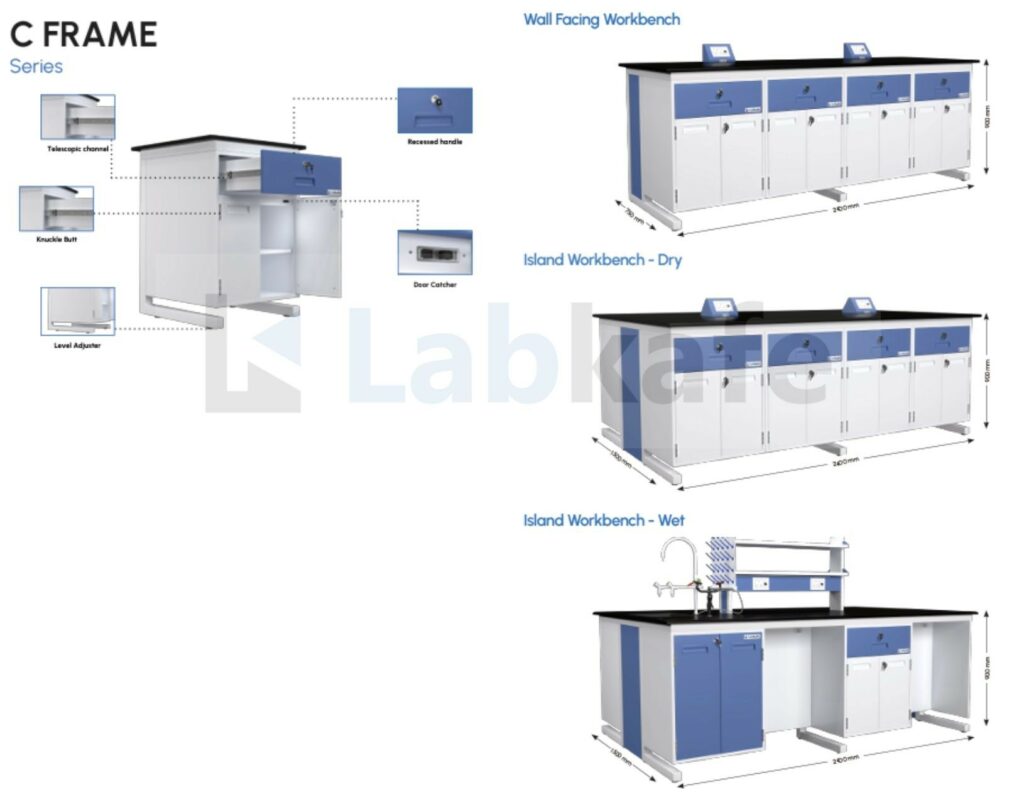

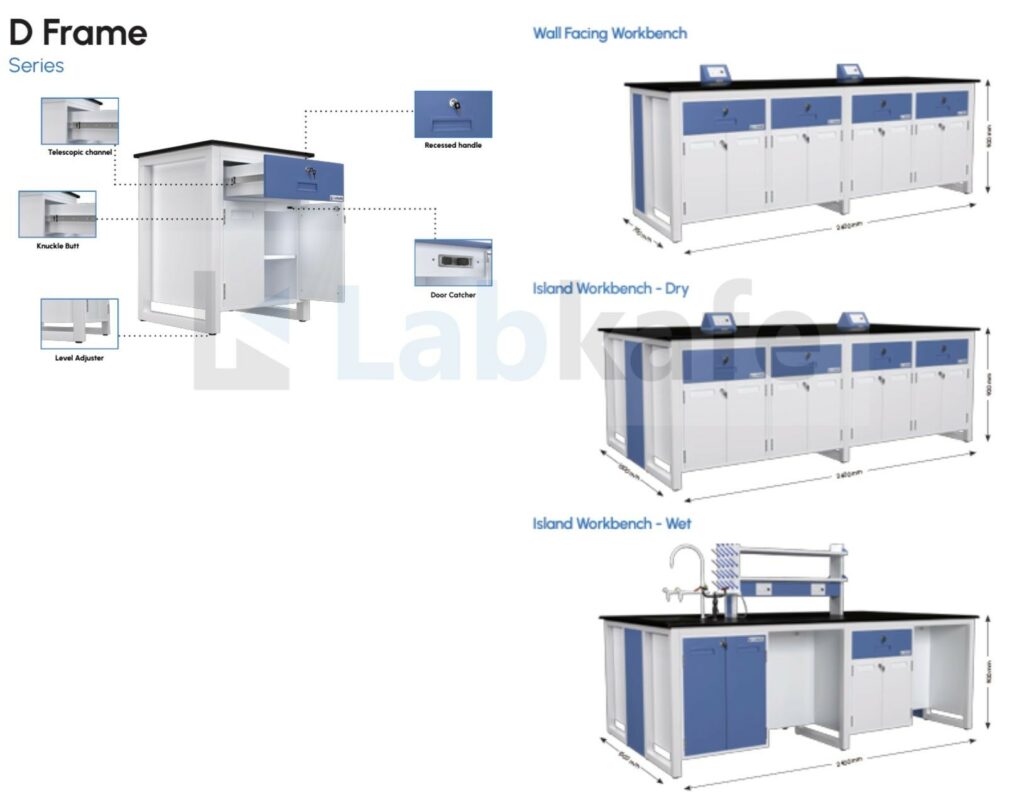
Regardless of lab type, heavy equipment requires furniture with high load-bearing capacity.
- For heavier apparatus like Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CROs), motor-generator kits, reflux units, and microscopes, a D-frame construction offers superior support.
- For lighter setups or flexible lab arrangements, especially in schools with space constraints, a C-frame construction can be used.
Layout and Arrangement Considerations for Wet vs Dry Lab Furniture
Wet Lab Furniture Layout
- Needs separate plumbing and gas pipelines
- Integrated sinks, burners, and safety fixtures are necessary
- Electrical instruments, if used, must be placed separately to ensure safety
- Reagent racks on tabletop benches can obstruct the teacher’s visibility during demonstrations
Thus, planning must factor in both utility lines and student visibility.
Dry Lab Furniture Layout
- Focuses on long benches or series-arranged tables for ease of access
- Allows group experiments with ample space to move and observe
- Furniture must support movement, data collection, and line-of-sight to the demonstration table
In physics labs, the teacher’s table must be centrally located and visible to all students.
Summary
The lab planning of wet vs dry lab furniture is different. To ensure that the lab can be used conveniently and reshaped easily later on to accommodate more work, it is important to create lab designs from professionals. Contact lab experts to find the best possible design for your wet or dry lab furniture setup.










Leave a Reply